Relocation Policy & Practice
Multiple Policy Types & Practices Leveraged, Traditional Assignments Remain Majority
As policy types expanded to meet the demands and constraints created by the Great Recession, corporate professionals took responsibility for more kinds of relocation programs. The vast majority of professionals continue to maintain formal policies for domestic (80%) and international relocations (80%); many others are managing policies for permanent international transfers (67%), international localization (66%) and short-term/temporary assignments (65%). More than half have international intra-regional (58%) and extended business travel policies (52%) in place as well, and 40% state a policy exists for long-distance commuter arrangements.
- Mid-size and large firms continue to be more likely to maintain policies for specialized arrangements outside general domestic and international policies. And they are more likely to maintain formal domestic and international policies overall.
- Besides an increasing variety of policies, most firms continue to define tiers or levels within policies. The larger the firm, the more likely its domestic policy will have a tiered structure. Firms using tiers, on average, manage two or more such policies across company size. Levels are based on a variety of factors; the top two across company size, domestically and internationally, are job/grade level and position/job title.
Question 17-1
Companies with a formal relocation policy: for domestic relocations
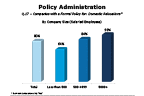
-- click to enlarge --
Question 17-2
Companies with a formal relocation policy: for short-term/ temporary assignments
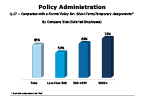
-- click to enlarge --
Question 17-3
Companies with a formal relocation policy: extended business travel

-- click to enlarge --
Question 17-4
Companies with a formal relocation policy: long-distance commuter
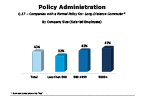
-- click to enlarge --
Question 18a-1-1
Does your company have different tiers within its domestic relocation policy...
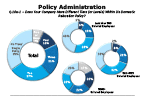
-- click to enlarge --
Question 18a-1-2
Average number of tiers (levels) within domestic relocation policy
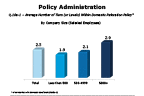
-- click to enlarge --
Question 18a-2-1
Does your company have different tiers within its temporary assignments relocation policy...
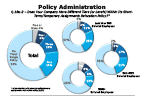
-- click to enlarge --
Question 18a-2-2
Average number of tiers (levels) within temporary assignments relocation policy
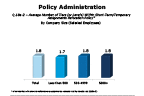
-- click to enlarge --
Question 18a-3-1
Does your company have different tiers within its extended business travel policy...
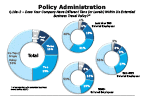
-- click to enlarge --
Question 18a-3-2
Average number of tiers (levels) within temporary extended business travel policy
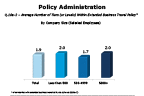
-- click to enlarge --
Question 18a-4-1
Does your company have different tiers within its long-distance commuter policy...
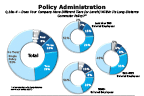
-- click to enlarge --
Question 18a-4-2
Average number of tiers (levels) within long-distance commuter policy
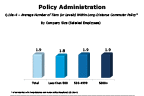
-- click to enlarge --
Question 18b-1
What are your different tiers based on...
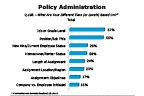
-- click to enlarge --
Question 18b-2
What are your different tiers based on...
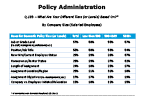
-- click to enlarge --
Question 43f-1
Companies with a formal policy for: International relocations
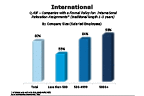
-- click to enlarge --
Question 43f-2
Companies with a formal policy for: Permanent transfers

-- click to enlarge --
Question 43f-3
Companies with a formal policy for: localization
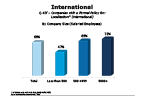
-- click to enlarge --
Question 43f-4
Companies with a formal policy for: intra-regional assignments
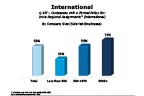
-- click to enlarge --
Question 43g-1-1
Does your company have different tiers within its international relo policy?
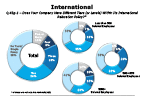
-- click to enlarge --
Question 43g-1-2
Average number of tiers within international relo policy
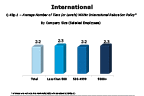
-- click to enlarge --
Question 43g-2-1
Does your company have different tiers within its permanent transfers policy
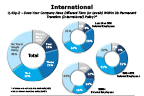
-- click to enlarge --
Question 43g-2-2
Does your company have different tiers within its permanent transfers policy
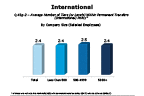
-- click to enlarge --
Question 43g-3-1
Does your company have different tiers within its localization policy
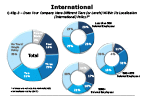
-- click to enlarge --
Question 43g-3-2
Does your company have different tiers within its localization policy
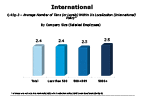
-- click to enlarge --
Question 43g-4-1
Does your company have different tiers within its intra-regional assignments policy
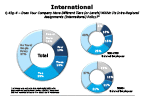
-- click to enlarge --
Question 43g-4-2
Does your company have different tiers within its intra-regional assignments policy
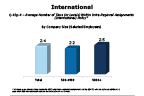
-- click to enlarge --
Question 43h-1
What are your different tiers based on?

-- click to enlarge --
Question 43h-2
What are your different tiers based on?
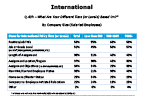
-- click to enlarge --
Candidate Assessments
Candidate assessments have gained widespread use over the past two years as a means to ensure successful relocations. In both 2015 and 2016, roughly three-fourths of firms assessed candidates prior to relocation, compared to around half of firms that performed some level of vetting the previous three years. Assessments for all relocations remains the most popular (46%), similar to last year (48%) and roughly double previous levels (21%, 2012-2014). Past years saw far more differences in the use of candidate assessments and types of implementation among firms of different sizes. This year, those differences are minimized and the usage levels overall for both assessments and implementation methods are mostly similar, regardless of company size.
Question 34-1
Does your organization perform candidate assessments prior to relocation offers

-- click to enlarge --
Question 34-2
Does your organization perform candidate assessments prior to relocation offers

-- click to enlarge --
Core/Flex Policy
Over the past two years, relocation volumes increased despite unique pressures from many sources. The incorporation of core/flex elements into policies is now nearly universal to allow for creative implementation. For 2015-2016, nearly 9 out of 10 firms use aspects of core/flex in policy, a decided increase over roughly three-fourths of firms in 2013-2014. And, over the past two years, the use of core/flex policy has reached similar levels at companies of all sizes. Previously, such tailoring of benefits was more likely in mid-size and large firms. Coverage for core components continues to be the most popular aspect across firms of all sizes (either across all employee levels/categories or depending on employee level/category). But percentages of firms in 2015-2016 offering flexible use, whether for the full relocation benefit or a portion of it, remain essentially doubled compared to 2013-2014, except for flexible use of a portion dependent on employee level/category, which returned close to previous levels.
Since coverage of core components is the most popular means of implementation, we dug a little deeper to see what types of costs it included. Overall, the top components are travel expenses (74%), temporary housing (67%), and household goods shipping (64%). The percentages of firms viewing travel expenses as core was nearly identical across company size, but differences emerged for other costs. Mid-size and large firms are a bit more likely to view temporary housing as a core benefit compared to small firms (74% and 68% vs. 59%). Large firms are more likely to see household goods shipping as core (76%) compared to mid-size or small firms (61% and 58%). Less than half of firms overall view storage, miscellaneous allowances, real estate assistance/transaction costs or rental assistance as core/flex benefits. However, company size plays a role in these elements as well. More mid-size and large firms see storage as a core benefit (47% and 56%) compared to small firms (37%). More large firms than mid-size or small firms see miscellaneous allowances (55% vs. 41% and 36%) as core.
Question 19a
Companies whose formal relocation policy utilizes aspects of core coverage/flex policy
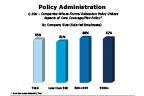
-- click to enlarge --
Question 19b-1
Aspects of core coverage/flex policy incorporated into relocation policy
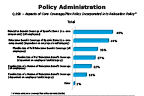
-- click to enlarge --
Question 19b-2
Aspects of core coverage/flex policy incorporated into relocation policy

-- click to enlarge --
Question 19c-1
Relocation costs considered core coverage/fixed benefits with relocation policy
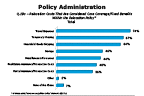
-- click to enlarge --
Question 19c-2
Relocation costs considered core coverage/fixed benefits with relocation policy
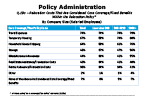
-- click to enlarge --
Incentives
While use of incentives dropped in 2013, they rebounded and leapt to historical highs in 2014 and 2015 with the vast majority of firms offering them. With employee reluctance rising to recessionary levels in 2014 and remaining elevated in 2015, tailoring policy to individual needs remains a key option in the toolbox of professionals. With housing/mortgage pressures subsiding as real estate stabilized, far fewer firms offered extended temporary housing in 2014-2015 than did in 2013 (58% and 57% vs. 72%). Yet this benefit remains one of the top three incentives over the past seven years. Relocation bonuses and cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs) in salary again round out the top three incentives across company size, similar to the past two years.
- Among large firms, 40% offered a guaranteed buyout option for origin homes last year, similar to 2014 (41%), and 32% offered a buyer value option, down from 42% in 2014. Smaller firms were much less likely to offer these. And, while 37% of large firms offered loss-on-sale protection in 2015, only around half as many mid-size firms (19%) and only around a fifth as many small firms (7%) offered this option.
Incentives continue to be highly successful in convincing employees to relocate: nine out of ten firms say incentives worked almost always or frequently, similar to historical levels.
Question 10a
Companies indicating they offered additional incentives to encourage employee relocations in 2015
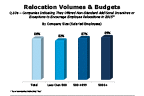
-- click to enlarge --
Question 10b-1
Additional incentives offered by companies to encourage employee relocations in 2015

-- click to enlarge --
Question 10b-2
Additional incentives offered by companies to encourage employee relocations in 2015
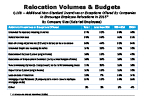
-- click to enlarge --
Question 10c
Frequency of incentives proving successful in convincing an employee to relocate
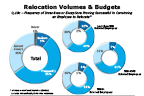
-- click to enlarge --
Cost Containment
With economic conditions still a factor, as well as the potential for market weakness even as relocation volumes have increased, cost containment remains popular for the second straight year after decreasing progressively in 2012-2013. The creative solutions adopted during the recession now appear to be key tools for the vast majority of firms, regardless of size, even as budgets recover. “Doing more with less” looks increasingly like the new normal with each passing year.
The use of cost containment methods in 2015 jumped to the highest level historically among large firms, similar to the levels recorded during the recession and first two years of recovery (84% vs. 78%-81%). Compared to previous historic levels, notably more small and mid-size firms used such tools in 2014-2015, although use among mid-size firms dropped notably from 2014 (74% vs. 84%). Generally, capping relocation benefit amounts remains the most popular method; most other methods saw usage remain higher than in 2013, even if they dipped below 2014 levels. The biggest shifts were in the use of pre-decision counseling, which remains nearly double that of 2013 (22% vs. 12%), and far fewer restructuring policy tiers/eligibility (18% vs. 30%) compared to 2014.
- Large firms tend to use more cost-containment methods than smaller firms overall. The biggest differences last year were the use of reviewing/renegotiating supplier contracts and offering pre-decision counseling. Large firms were far more likely than mid-size or small firms to use these measures (36% vs. 21% and 17%, 33% vs. 19% and 17%, respectively). Additionally, large firms were much more likely than small firms to modify COLA offering policy (24% vs. 7%).
Question 21-1
Cost containment measures that could have been used in relocation policy/practice in 2015
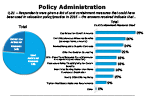
-- click to enlarge --
Question 21-2
Cost containment measures in relocation policy/practice used in 2015
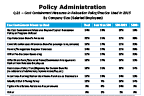
-- click to enlarge --
Alternative Assignments
Although not typical historically, the majority of firms used arrangements outside traditional relocations in the past two years. Roughly two-thirds of firms now use alternative assignments (64%), similar to last year (65%) and far more often than in the previous three years. The percentages of large firms using such arrangements progressively increased from 2012 to 2014 (60%, 62%, 66%) and remains on par with 2015 this year (72% vs. 73%). Usage among mid-size firms remains nearly twice that of 2014 (68% vs. 37%) and similar to 2015 (75%), while usage among small firms inches upwards again over last year (54% vs. 48%) and continues to be more than twice that recorded in 2014 (19%).
The mobility policy methods for alternative assignments vary widely. In the past, achieving strategic business goals was the overwhelming policy driver. Now, usage levels are similar for most methods. Nearly every potential policy method is used by roughly a third or more of all firms. However, a few differences appear across company size. Far more small and mid-size firms than large firms use alternative assignments in place of traditional short-term assignments (41% and 39% vs. 19%). And large firms are more likely than small and mid-size firms to use alternative assignments in addition to traditional short-term arrangements (29% vs. 17% and 13%).
This year the survey added business need as a choice for the question about what key factors determine alternative assignment use. Roughly two-thirds of firms across company size saw it as the top consideration; around half of firms overall chose assignment purpose, job function and cost. Assignment purpose dropped last year compared to previous levels (53% vs. 66%+) and dips slightly more this year (48%), with a similar decline occurring for cost (44% vs. 51%, 54% and 64%). Job function dips as well for the first time from historically higher levels (45% vs. 53%+), supporting the notion that business planning now drives alternative assignments more than operational concerns do.
Question 27-1
Is your company utilizing "Alternative Assignments"...
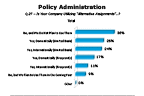
-- click to enlarge --
Question 27-2
Is your company utilizing "Alternative Assignments"...

-- click to enlarge --
Question 27a-1
How are "Alternative Assignment" arrangements incorporated into your organization's overall employee mobility strategy?
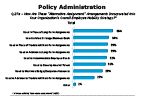
-- click to enlarge --
Question 27a-2
How are "Alternative Assignment" arrangements incorporated into your organization's overall employee mobility strategy?
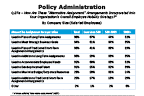
-- click to enlarge --
Question 27b-1
Key factors determining "Alternative Assignment" use
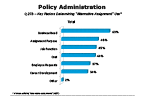
-- click to enlarge --
Question 27b-2
Key factors determining "Alternative Assignment" use
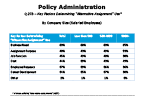
-- click to enlarge --